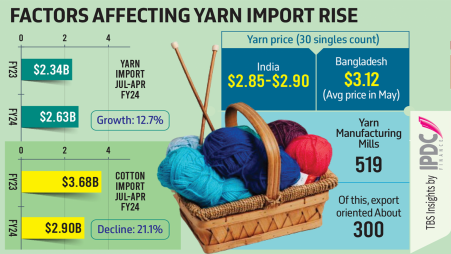
Bangladesh’s textile and spinning mills are struggling to produce yarn due to a lingering gas crisis which has led to a jump in yarn imports of about 13% as fabric and apparel makers look elsewhere to meet the demand.
The headline ” import jumps 13% as local production chokes amid gas crisis” suggests several key points:
- Yarn Import Increase: There has been a significant increase (13%) in the import of yarn. is an essential material in textiles and garment manufacturing.
- Local Production Issues: Local production of yarn is facing challenges, likely due to the ongoing gas crisis. This could imply that local yarn manufacturers are struggling with energy supply issues, particularly if their production processes are heavily reliant on gas.
- Impact on Textile Industry: The increase in yarn imports indicates that local textile manufacturers may not be able to meet demand solely through domestic production. This could potentially lead to higher costs for manufacturers who now have to import yarn instead of sourcing it locally.
- Economic Implications: Importing yarn instead of producing it locally can have economic implications, such as increased costs due to import tariffs, transportation expenses, and currency exchange rates.
In summary, the headline highlights a specific economic situation where a gas crisis is affecting local production, leading to increased imports and potential challenges for the textile industry.
Certainly! Let’s delve deeper into each aspect mentioned in the headline:
1. Yarn Import Increase
is a crucial raw material in the textile industry, used in the production of fabrics and garments. When there is an increase in yarn imports, it typically indicates that local supply is insufficient to meet demand. This could be due to various reasons such as:
- Capacity Constraints: Local manufacturers may not have sufficient production capacity to meet the growing demand from textile manufacturers.
- Quality Considerations: Imported might be preferred due to better quality or specific characteristics that are not available locally.
- Cost Considerations: Sometimes, imported yarn could be cheaper than domestically produced yarn, especially if the local production costs are higher due to factors like energy prices or labor costs.
2. Local Production Issues
The headline suggests that local production of is facing challenges, primarily due to a gas crisis. This could mean:
- Energy Supply Constraints: Yarn production often requires significant energy inputs, particularly if the production processes involve spinning, dyeing, or other energy-intensive activities. A gas crisis would directly impact industries that rely on natural gas for operations.
- Operational Disruptions: If local yarn manufacturers rely heavily on gas for their operations and there are shortages or price spikes in gas supply, it can disrupt production schedules and output levels.
3. Impact on Textile Industry
The textile industry is a major consumer of yarn. Therefore, any disruption in local production can have ripple effects:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Textile manufacturers may face delays or shortages in yarn supply, impacting their ability to fulfill orders on time.
- Cost Increases: Depending on the cost differential between imported and locally produced yarn, textile manufacturers may face increased production costs, affecting their profitability.
- Competitiveness: If imported yarn becomes cheaper or more readily available than local yarn, it could affect the competitiveness of local textile manufacturers in both domestic and international markets.
4. Economic Implications
The economic implications of increased yarn imports and local production issues include:
- Trade Balance: Increased imports can affect the trade balance of a country if the value of imports exceeds the value of exports.
- Foreign Exchange Impact: Importing requires foreign currency, which can impact a country’s foreign exchange reserves and currency exchange rates.
- Policy Considerations: Governments may need to consider policy interventions such as subsidies, tariffs, or incentives to support local production and reduce dependency on imports.
Overall, the headline points to a complex interplay of factors affecting the textile industry, including energy supply issues, production dynamics, and economic implications at both local and national levels.
Certainly! Let’s explore further details and implications of the situation described in the headline ” import jumps 13% as local production chokes amid gas crisis”:

1. Yarn Import Trends
- Market Demand: The increase in yarn imports by 13% indicates a robust demand for yarn in the domestic market. This could be driven by various factors such as growth in the textile and apparel industry, seasonal demand fluctuations, or shifts in consumer preferences.
- Source of Imports: Understanding where the yarn imports are coming from can provide insights into trade relationships and global supply chains. Countries with competitive advantages in production, such as lower production costs or advanced technology, may dominate the import market.
2. Challenges in Local Production
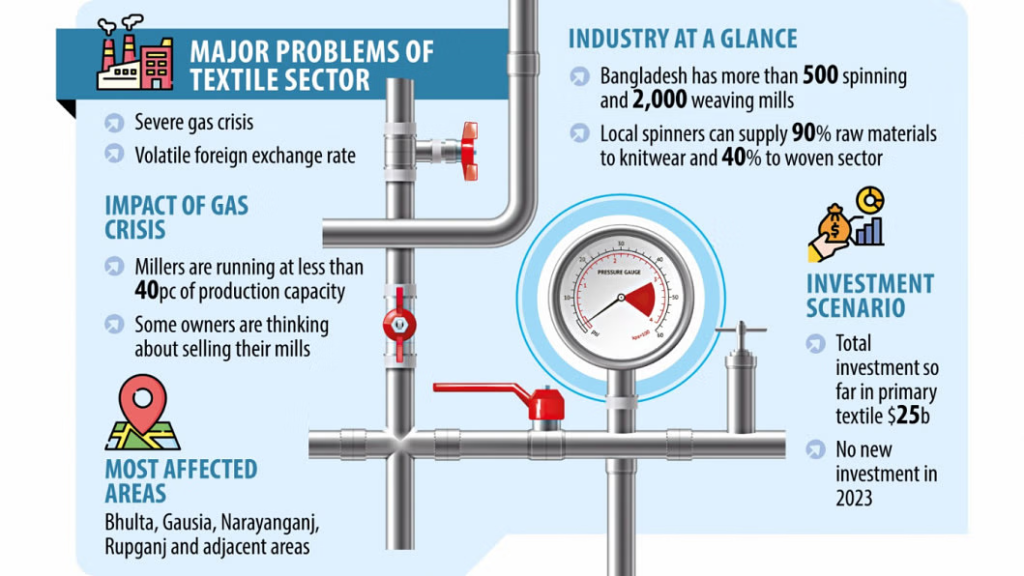
- Gas Crisis Impact: The mention of a gas crisis suggests that local yarn production is heavily reliant on natural gas for energy. Gas shortages or price increases can severely disrupt production schedules, increase operating costs, and reduce profitability for local manufacturers.
- Technological and Infrastructure Constraints: Local yarn producers may also face challenges related to outdated technology, inadequate infrastructure, or insufficient investment in capacity expansion. These factors can limit their ability to meet growing demand efficiently.
3. Impact on Textile Sector
- Supply Chain Disruptions: serves as a fundamental input for the textile industry. Any disruption in yarn supply can ripple through the entire supply chain, affecting textile manufacturers’ production schedules and ability to meet customer orders.
- Employment and Economic Contribution: The textile sector is a significant contributor to employment and economic growth in many countries. Challenges in local yarn production could impact job stability and economic activity in related industries.
- Competitiveness: Increased reliance on imported yarn may affect the competitiveness of domestic textile manufacturers. Factors such as higher import costs, quality differences, and supply chain reliability can influence their ability to compete in global and domestic markets.
4. Economic and Policy Considerations
- Trade Balances: A significant increase in yarn imports could widen the trade deficit if the value of imports surpasses the value of exports. This can impact the overall balance of payments and foreign exchange reserves.
- Policy Responses: Governments may consider policy interventions to support local yarn production, such as subsidies for energy-efficient technologies, investment incentives for modernization, or tariffs on imported to protect domestic industries.
- Long-term Sustainability: Ensuring a stable and resilient production sector is crucial for the long-term sustainability of the textile industry. This may require coordinated efforts from governments, industry stakeholders, and financial institutions to address structural challenges and promote growth.
In conclusion, the headline reflects a complex interplay of economic, industrial, and policy factors affecting the and textile industries amid a gas crisis. Understanding these dynamics is essential for stakeholders to navigate challenges, optimize supply chains, and promote sustainable growth in the textile sector.
ertainly! Let’s explore further details and implications of the situation described in the headline ” import jumps 13% as local production chokes amid gas crisis”:
ons related to the topic of the headline ” import jumps 13% as local production chokes amid gas crisis”:
1. Why is there a gas crisis impacting local yarn production?
Answer: The gas crisis can impact local production because natural gas is often used as an energy source in the manufacturing process of . Shortages or price increases in natural gas can disrupt production schedules, increase operating costs, and reduce the competitiveness of local producers.
2. What are the implications of increased yarn imports?
Answer: Increased imports can have several implications:
- It may indicate that local production is unable to meet domestic demand, potentially due to capacity constraints, technological limitations, or cost disadvantages.
- It could affect the trade balance if the value of yarn imports exceeds the value of yarn exports, impacting the overall economy.
- It may influence the competitiveness of domestic textile manufacturers depending on factors like import costs, quality differences, and supply chain reliability.
3. How does the yarn import increase affect the textile industry?
Answer: The increase in imports affects the textile industry in various ways:
- It can lead to supply chain disruptions if local manufacturers face shortages or delays in obtaining yarn.
- It may increase production costs for textile manufacturers who now rely on imported yarn, impacting their profitability.
- It could influence employment and economic activity within the textile sector, which is a significant contributor to many economies worldwide.
4. What are potential policy responses to support local yarn production?
Answer: Governments may consider several policy responses to support local yarn production amid challenges like a gas crisis:
- Providing subsidies or incentives for energy-efficient technologies to reduce production costs.
- Investing in infrastructure and capacity expansion to enhance domestic production capabilities.
- Implementing tariffs or import quotas to protect domestic industries from cheaper imported yarn.
- Encouraging research and development in yarn production technologies to improve competitiveness and sustainability.
5. How can stakeholders in the textile industry mitigate the impact of yarn import increases and local production issues?
Answer: Stakeholders in the textile industry can mitigate the impact through:
- Diversifying sourcing strategies for yarn to reduce dependency on a single supplier or country.
- Investing in technology and innovation to improve efficiency and reduce production costs.
- Advocating for policies that support local manufacturing and ensure a stable supply of raw materials.
- Collaborating with government and industry associations to address systemic challenges and promote sustainable growth.
These FAQs provide a broad overview of the issues surrounding yarn imports, local production challenges, and their implications for the textile industry amid a gas crisis. They aim to clarify common questions and shed light on potential strategies for stakeholders to navigate and address these complex issues effectively.
The situation described in the headline ” import jumps 13% as local production chokes amid gas crisis” poses several threats to the textile industry and broader economic stability:
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Dependence on imported exposes textile manufacturers to supply chain vulnerabilities, including disruptions in global trade, geopolitical tensions, and fluctuations in exchange rates. Any disruption in imports could lead to delays in production and fulfillment of orders.
- Increased Costs: Importing may increase production costs for textile manufacturers due to factors such as transportation expenses, import tariffs, and currency exchange rates. This can reduce profit margins and competitiveness in both domestic and international markets.
- Impact on Employment: If local yarn production continues to decline or face challenges amid the gas crisis, it could lead to job losses within the textile industry. Textile manufacturing is a significant source of employment in many countries, and disruptions in production could have socio-economic implications.
- Trade Imbalance: A sustained increase in yarn imports without a corresponding increase in exports could widen the trade deficit for countries heavily reliant on textile exports. This imbalance could strain foreign exchange reserves and impact overall economic stability.
- Dependency Risks: Overreliance on imported yarn exposes countries to risks related to supply chain dependencies. Disruptions in -producing countries, regulatory changes, or shifts in global trade policies could disrupt the supply of imported , affecting local manufacturing capabilities.
- Competitiveness Challenges: Local textile manufacturers may face challenges in competing with international counterparts who have access to cheaper or higher-quality . This could erode market share and weaken the overall competitiveness of the domestic textile industry.
- Policy and Regulatory Risks: Changes in import tariffs, trade policies, or regulatory frameworks governing yarn imports could further impact the cost and availability of imported . Uncertainty in policy environments can create challenges for long-term planning and investment in the textile sector.
To mitigate these threats, stakeholders in the textile industry and policymakers may need to consider strategies such as diversifying sourcing channels, investing in domestic production capabilities, promoting innovation in yarn manufacturing technologies, and advocating for supportive policies that enhance the resilience and competitiveness of the sector.
Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of the situation described in the headline “Yarn import jumps 13% as local production chokes amid gas crisis”:
Advantages:
- Meeting Demand: Increased imports can help meet the growing demand for textiles and garments when local production capacity is insufficient. This ensures that textile manufacturers can continue to fulfill orders and maintain production schedules.
- Diversification of Supply: Importing yarn diversifies the supply chain, reducing dependency on a single source or region. This can mitigate risks related to local production disruptions, natural disasters, or geopolitical tensions affecting domestic production.
- Cost Efficiency: In some cases, imported may be more cost-effective than domestically produced , especially if it benefits from economies of scale, lower production costs abroad, or favorable exchange rates. This can lower overall production costs for textile manufacturers.
- Access to Specialized Yarn: Imports may provide access to specialized types of or higher-quality materials that are not available locally. This can enable textile manufacturers to produce higher-value products or meet specific customer requirements more effectively.
- Market Competitiveness: Access to a broader range of types and qualities through imports can enhance the competitiveness of local textile manufacturers in both domestic and international markets. This is particularly advantageous when competing with global rivals.
Disadvantages:
- Vulnerability to Supply Chain Risks: Dependence on imported makes textile manufacturers vulnerable to supply chain disruptions, such as trade disputes, transportation issues, or sudden changes in import regulations. This can lead to delays in production and increased uncertainty.
- Currency Exchange Risks: Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the cost of imported yarn, potentially leading to unpredictable costs for textile manufacturers. This adds a layer of financial risk and can affect profit margins.
- Trade Imbalances: A significant increase in yarn imports without a corresponding increase in exports can widen the trade deficit for countries reliant on textile exports. This imbalance may strain foreign exchange reserves and impact overall economic stability.
- Loss of Domestic Industry: Heavy reliance on imported may lead to the decline or underinvestment in domestic production capabilities. This can negatively affect employment in the local textile industry and reduce the sector’s contribution to the economy.
- Quality Control and Standards: Ensuring consistent quality and adherence to industry standards can be challenging when relying on imported yarn. Differences in manufacturing practices, regulatory compliance, or product specifications may pose quality control issues for textile manufacturers.
- Long-term Sustainability Concerns: Over-reliance on imported inputs, such as , may raise concerns about the long-term sustainability and resilience of the textile industry. It may limit opportunities for technological innovation and local value addition.
In conclusion, while importing yarn offers advantages such as meeting demand, diversifying supply, and accessing cost-effective materials, it also presents challenges related to supply chain risks, currency fluctuations, trade imbalances, and impacts on domestic industry. Balancing these factors requires strategic planning, risk management, and policy interventions to foster a competitive and sustainable textile sector.
Certainly! Here’s the bottom line regarding the situation described in the headline “Yarn import jumps 13% as local production chokes amid gas crisis”:
Bottom Line:
- Immediate Supply Solution: Increased imports provide a short-term solution to meet immediate demand when local production faces challenges, such as those exacerbated by a gas crisis.
- Dependency Risks: Heavy reliance on imported yarn exposes the textile industry to supply chain vulnerabilities, currency fluctuations, and regulatory changes that can disrupt production and increase costs.
- Economic Implications: The trade-off between importing yarn and supporting local production impacts economic stability, trade balances, and employment within the textile sector.
- Strategic Considerations: Balancing import reliance with investments in domestic production capabilities, innovation, and policy support is crucial for long-term competitiveness and resilience.
- Policy and Industry Response: Governments and industry stakeholders need to collaborate on strategies that mitigate risks, promote sustainable growth, and ensure a robust textile industry that can adapt to global challenges.
In essence, while importing yarn can alleviate immediate supply shortages, it’s essential to manage the associated risks and strategically invest in strengthening domestic production capabilities to maintain a resilient and competitive textile sector.



